1. Introduction
South Korea’s measures to restrict the use of hazardous substances in electronic and electrical products (EEPs) are mainly based on the Act on Resource Circulation of Electrical and Electronic Equipment and Vehicles (commonly known as Korea RoHS, hereinafter refers to Act on Resource Circulation of Electronic Products, etc.), as well as its enforcement decree and enforcement rules.
The Act on Resource Circulation of Electronic Products, etc. was issued as Act No. 8405 on April 27th, 2007, and entered into effect on January 1st, 2008. The purpose of the Act is to establish a resource recycling system for the efficient use of resources and contribute to environmental conservation and the sound growth of the national economy by placing restrictions on the use of hazardous substances. The Act stipulates the responsibilities for the authorities, manufacturers, importers, recyclers, and citizens to control the hazardous substances in EEPs and vehicles and properly treat and recycle the waste of these products.
Compared with the EU RoHS, which is nearly applicable to all consumer EEPs, Korea’s restrictions on the use of hazardous substances is only for 26 specified kinds of EEPs. In addition, EU RoHS has taken the 4 kinds of phthalate esters, namely DEHP, BBP, DBP, and DIBP, into concern as the restricted hazardous substance, while Korea RoHS has not. To make sure that the domestic regulations keep pace with the international standards, a new legislative notice was issued on July 8th, 2020, by the Ministry of Environment (MoE) to solicit public comments on the amendment to the Enforcement Decree of the Act which would expand the Act’s regulatory scope by taking more kinds of EEPs and hazardous substances into consideration. (ChemLinked News)
On November 16th, 2020, the amendment to the Enforcement Decree of Act on Resource Circulation of Electronic Products, etc. was approved. The supplementation of 23 kinds of electrical and electronic will take effect from January 1st, 2021, and the 4 kinds of phthalate esters in the products will be restricted from July 1st, 2021. (ChemLinked News)
2. Regulatory Scope
2.1 Hazardous substances restricted to use in the EEPs
Currently, there are 26 kinds of products subject to the restrictions. According to the amendment, 23 kinds of new electrical and electronic products which amounts of use have increased greatly in recent years, and that have a great impact on public health and environment will be added as target products subject to restrictions on the use of hazardous substances.
Current | Content standards | Amendment | Content standards |
1. Lead | Less than 0.1% by weight (wt) in the same substance | 1. Lead | Less than 0.1% by weight (wt) in the same substance |
2. Mercury | 2. Mercury | ||
3. Hexavalent chromium | 3. Hexavalent chromium | ||
4. Polybrominated biphenyls | 4. Polybrominated biphenyls | ||
5. Poly brominated diphenyl ethers | 5. Poly brominated diphenyl ethers | ||
6. Cadmium | Less than 0.01% by weight (wt) in the same substance | 6. Diethylhexyl phthalate (DEHP) | |
7. Benzyl butyl phthalate (BBP) | |||
8. Dibutyl phthalate (DBP) | |||
9. Diisobutyl phthalate (DIBP) | |||
10.Cadmium | Less than 0.01% by weight (wt) in the same substance |
2.2 Scope of EEPs subject to restrictions on the use of hazardous substances
Table 1. EEPs Subject to the Restrictions on the Use of Hazardous Substances
Category | Kinds |
Current (26 kinds) | Television, refrigerator, washing machine, air conditioner, personal computer, printer, copying machine, fax machine, electric water purifier, electric oven, microwave oven, food processor, tableware dryer (including dishwasher), electric bidet, air purifier, electric heater, loudspeaker box, electric rice cooker, water softener, humidifier, electric iron, electric fan, blender, dust collector, video player, and mobile telephone terminal |
To be added (23 kinds) | Vending machine, avigraph, wired and wireless router, treadmill, scanner, food dryer, drug-decocting machine, electronic frying pan, video game machine, electric water heater, foot bath machine, sewing machine, bread maker, dehumidifier, coffee maker, dehydrator, toaster, fryer, hair dryer, projector, electric massager, monitor camera, and electric kettle. |
The products scope is expanded gradually:

3. Obligations
3.1 Obligations on the restrictions of hazardous substances
In order to facilitate the recycling of EEPs and to minimize their harmful impact on the environment, every manufacturer or importer of the specified kinds of EEPs shall comply with the corresponding content limits above at the manufacturing stage. While for the products deemed impossible to remove hazardous substances due to their characteristics or no substitute is available, or the products for research, development, or exportation, the requirements shall not apply. (Article 9 of the Act) More specific exempt conditions for the restrictions on hazardous substances, please refer to Appendix 2 of the Enforcement Decree of the Act.
The manufacturers and importers shall publicly disclose whether they comply with the content limits of hazardous substances or the annual recyclability rate under the Act by either of the following methods:
Posting it on the operation management information system under the Act (www.ecoas.or.kr) , or;
Posting it on the website operated and managed by the manufacturer or importer of the EEPs;
The manufacturers shall publicly disclose such compliance information within 3 months from the date of releasing the EEPs to the market, and the importers shall disclose the information within 3 months from the import declaration date.
3.2 Obligations on the purpose of resource circulation
Since the main purpose of the Act is to promote the recirculation of EEPs and vehicles, most of the obligations for the manufacturers and importers are related to the recycling of their products. The followings are the responsibilities for the business operators according to Article 5 of the Act:
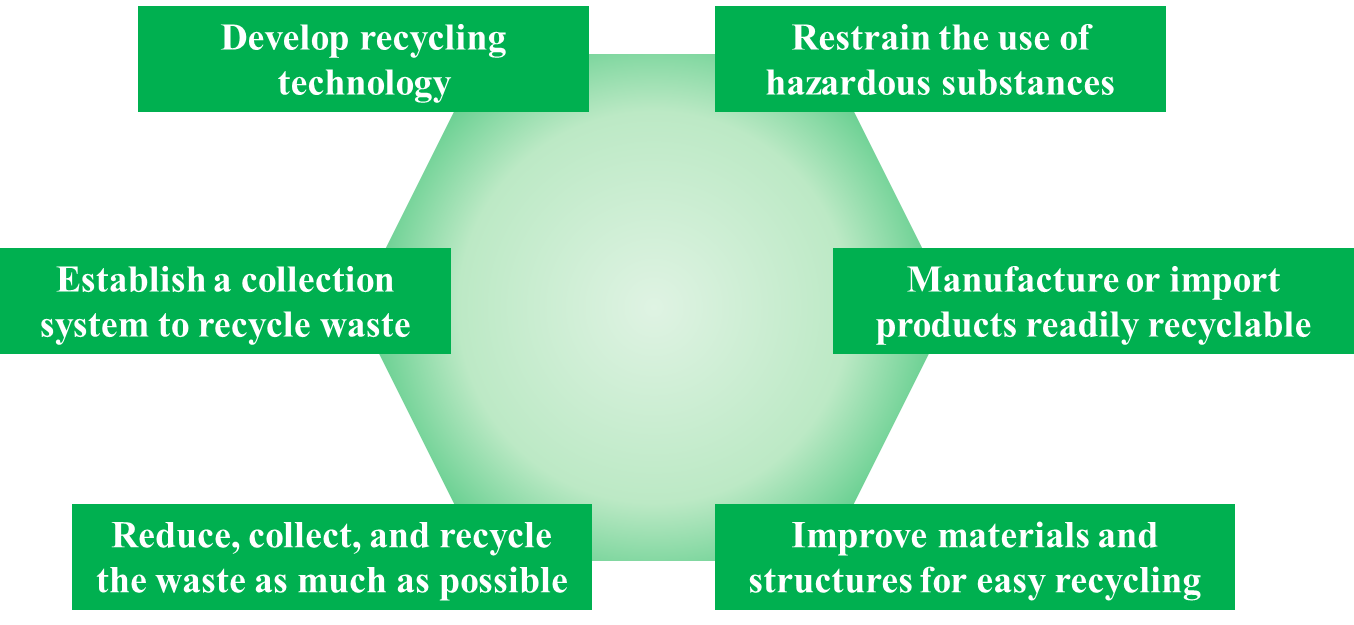
a. Manufacturers and importers
b. Distributors
Ensure that recyclable resources are circulated efficiently by endeavoring in earnest to collect waste electrical and electronic equipment.
c. Recyclers
Ensure that as many recyclable resources are recycled as much as possible so as to save resources and that such resources are used in an efficient manner.
d. Treatment business operators
Persons who run a business of treating environmental pollutants in waste EEPs or vehicles shall endeavor to minimize their impact on the environment.
Manufacturers or importers, distributors of EEPs, recyclers, and treatment business operators shall cooperate in the measures taken by the State or local governments to attain the purpose of this Act.
4. Resources
[News] 30-07-2020 South Korea to Strengthen the Management of Hazardous Substances in EEPs






